摘要
项目依赖环境太多,需要一个一个编译安装然后再做依赖,正好一个一个记录一下过程和出现的问题。
安装mingw
下载lapack库
lapack官网
lapack官网下载列表
lapck-3.11.tar.gz直接下载地址(github)
lapack-3.11.tar.gz本站下载地址
cmake配置
- Configure 选中
MinGW Makefiles - 处理配置项
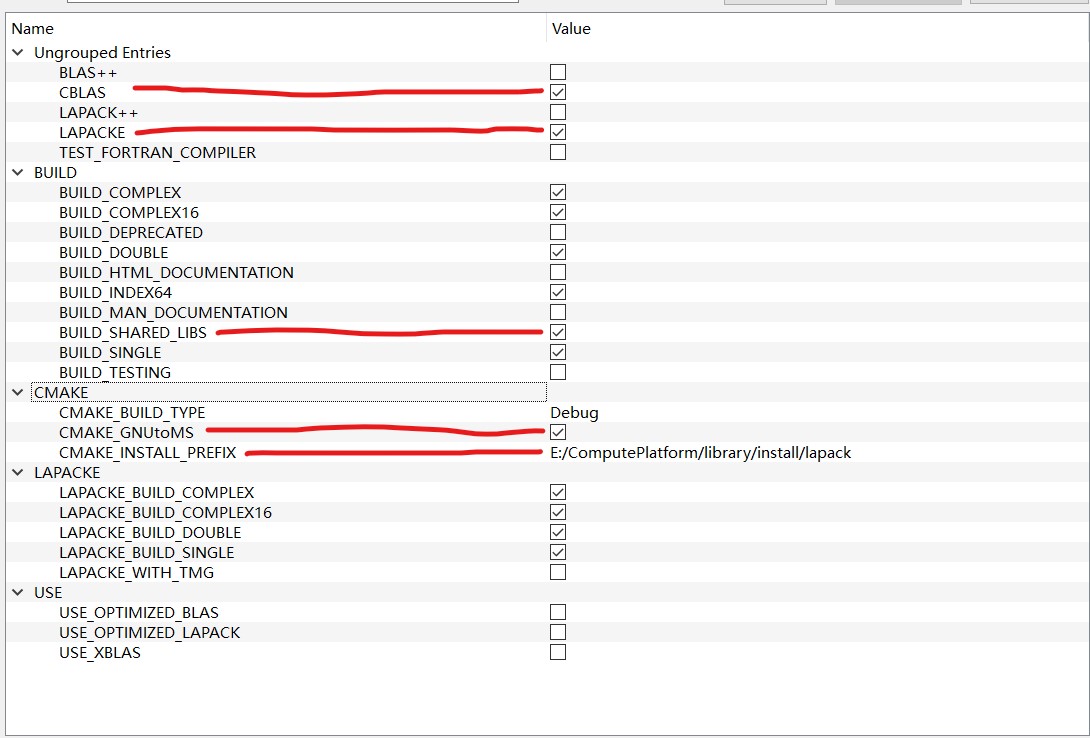
- Configure && Generate
编译及安装
1. cd build目录
2. mingw32-make.exe -j 8
3. mingw32-make.exe -j 8 install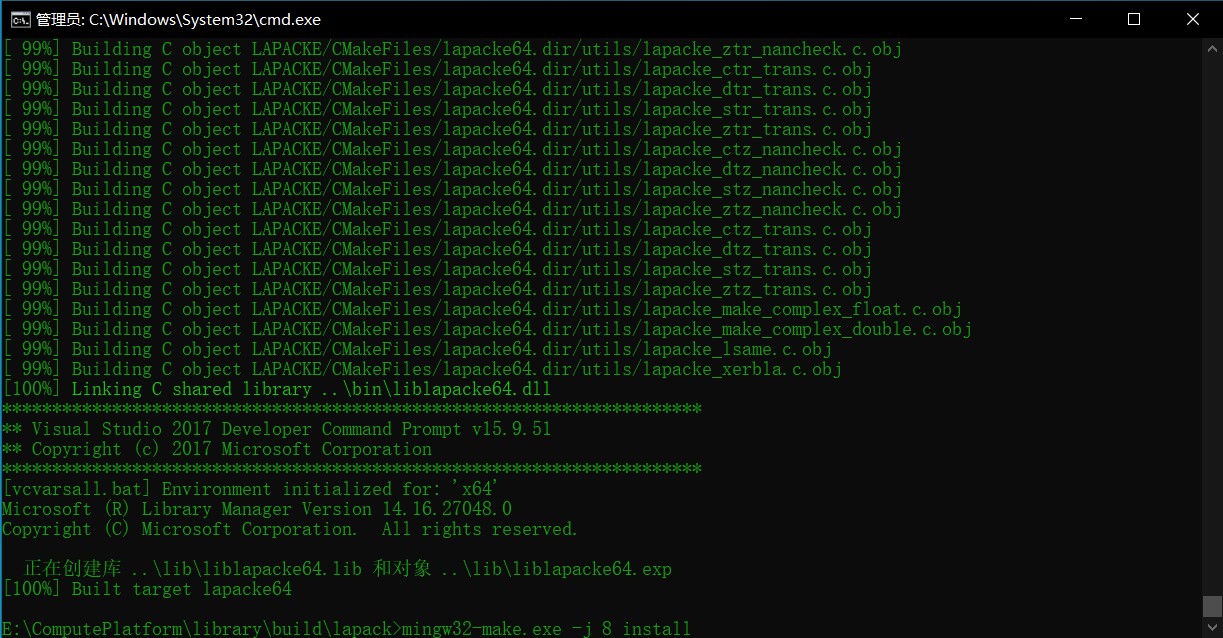
报错处理(多重定义问题)
[ 14%] Building Fortran object SRC/CMakeFiles/lapack64.dir/zlassq.f90.obj
[ 14%] Linking Fortran shared library ..\bin\liblapack64.dll
E:/program/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/libgfortran.a(string_intrinsics.o):(.text$_gfortran_concat_string+0x0): multiple definition of `_gfortran_concat_string'
../lib/libblas64.dll.a(d000008.o):(.text+0x0): first defined here
E:/program/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/libgfortran.a(string_intrinsics.o):(.text$_gfortran_string_len_trim+0x0): multiple definition of `_gfortran_string_len_trim'
../lib/libblas64.dll.a(d000038.o):(.text+0x0): first defined here
E:/program/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/libgfortran.a(transfer.o):(.text$_gfortran_transfer_integer_write+0x0): multiple definition of `_gfortran_transfer_integer_write'
../lib/libblas64.dll.a(d000058.o):(.text+0x0): first defined here
E:/program/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/libgfortran.a(transfer.o):(.text$_gfortran_transfer_character_write+0x0): multiple definition of `_gfortran_transfer_character_write'
../lib/libblas64.dll.a(d000053.o):(.text+0x0): first defined here
E:/program/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/libgfortran.a(transfer.o):(.text$_gfortran_st_write+0x0): multiple definition of `_gfortran_st_write'
../lib/libblas64.dll.a(d000032.o):(.text+0x0): first defined here
E:/program/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/libgfortran.a(transfer.o):(.text$_gfortran_st_write_done+0x0): multiple definition of `_gfortran_st_write_done'
../lib/libblas64.dll.a(d000033.o):(.text+0x0): first defined here
collect2.exe: error: ld returned 1 exit status
mingw32-make.exe[2]: *** [SRC\CMakeFiles\lapack64.dir\build.make:28718: bin/liblapack64.dll] Error 1
mingw32-make.exe[1]: *** [CMakeFiles\Makefile2:304: SRC/CMakeFiles/lapack64.dir/all] Error 2
mingw32-make.exe: *** [Makefile:155: all] Error 2解决办法
在build/lapack/SRC/CMakeFiles/lapack64.dir/link.txt文件中gfortran配置参数中添加--allow-multiple-definition参数
E:\program\mingw64\bin\gfortran.exe -frecursive -fdefault-integer-8 -g -shared -o ..\bin\liblapack64.dll -Wl,--out-implib,..\lib\liblapack64.dll.a -Wl,--major-image-version,3,--minor-image-version,11 -Wl,--whole-archive CMakeFiles\lapack64.dir/objects.a -Wl,--no-whole-archive @CMakeFiles\lapack64.dir\linkLibs.rsp -Wl,--allow-multiple-definition,--output-def,lapack64.def然后重新编译就能过了。