简介
直接用c的代码写呢太麻烦,用官网的c++用例写呢还乱码,逼得我只能自己写个类来处理了,要不写的东西太多,c的太繁琐,所以自己封装个类方便调用。
hdf5 封装c++ 类
#ifndef _OPEN_HDF5_
#define _OPEN_HDF5_
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <typeinfo>
#include "h5Cpp.h"
using namespace std;
struct H5TITLE{
string name;
string type;
};
/******** ATTR ********/
class CRattr
{
private:
hid_t hand_id;
public:
CRattr(hid_t id){
hand_id = id;
};
~CRattr(){};
template <class T>
shared_ptr<CRattr> attr(string key, T value, int len=1){
hid_t attr_type, attr_space;
hsize_t attr_dims[1] = { len };
char* value2 = new char(len);
if(typeid(T) == typeid(string) || typeid(T) == typeid(char*)){
attr_type = H5Tcopy(H5T_C_S1);
H5Tset_size(attr_type, H5T_VARIABLE);
}else if(typeid(T) == typeid(int)){
attr_type = H5T_NATIVE_INT;
}else if(typeid(T) == typeid(double)){
attr_type = H5T_NATIVE_DOUBLE;
}else{
return NULL;
}
attr_space = H5Screate_simple(1, attr_dims, NULL);
hid_t attr = H5Acreate(hand_id, key.c_str(), attr_type, attr_space, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
if(typeid(T) == typeid(string) || typeid(T) == typeid(char*)){
H5Awrite(attr, attr_type, value2);
}else{
H5Awrite(attr, attr_type, value);
}
shared_ptr<CRattr> tmp = make_shared<CRattr>(hand_id);
return tmp;
}
};
/******** DATA ********/
class CRdata
{
private:
hid_t hand_id;
string dataset_name;
public:
CRdata(hid_t id, string name){
hand_id = id;
dataset_name = name;
};
~CRdata(){};
template <class T>
shared_ptr<CRattr> insert(int len, T* wdata, vector<H5TITLE> &title){
herr_t status;
hsize_t dims[1] = { len };
hid_t memtype, space, dset, strtype = H5Tcopy(H5T_C_S1);
status = H5Tset_size(strtype, H5T_VARIABLE);
status = H5Tset_cset(strtype, H5T_CSET_UTF8);
memtype = H5Tcreate(H5T_COMPOUND, sizeof(T));
int sizet = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < title.size(); i++)
{
if (title.at(i).type == "string" || title.at(i).type == "char") {
H5Tinsert(memtype, title.at(i).name.c_str(), sizet, strtype);
} else if (title.at(i).type == "double") {
H5Tinsert(memtype, title.at(i).name.c_str(), sizet, H5T_NATIVE_DOUBLE);
} else if (title.at(i).type == "int") {
H5Tinsert(memtype, title.at(i).name.c_str(), sizet, H5T_NATIVE_INT);
}
sizet += sizeof(char*);
}
space = H5Screate_simple(1, dims, NULL);
// 创建数据集
dset = H5Dcreate(hand_id, dataset_name.c_str(), memtype, space, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
// 插入数据
status = H5Dwrite(dset, memtype, H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, wdata);
shared_ptr<CRattr> tmp = make_shared<CRattr>(dset);
return tmp;
};
template <class T>
shared_ptr<CRattr> insertList(int rows, int cols, T* wdata){
hid_t space, dset;
hid_t memtype;
if (typeid(T) == typeid(double)) {
memtype = H5T_NATIVE_DOUBLE;
} else if (typeid(T) == typeid(long double)){
memtype = H5T_NATIVE_LDOUBLE;
} else {
memtype = H5T_NATIVE_INT;
}
hsize_t dims[] = { rows, cols };
space = H5Screate_simple(2, dims, NULL);
// 创建数据集
dset = H5Dcreate(hand_id, dataset_name.c_str(), memtype, space, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
// 插入数据
herr_t status = H5Dwrite(dset, memtype, H5S_ALL, H5S_ALL, H5P_DEFAULT, wdata);
shared_ptr<CRattr> tmp = make_shared<CRattr>(dset);
return tmp;
};
};
/******** GROUP ********/
class CRgroup
{
private:
hid_t hand_id;
public:
CRgroup(hid_t id){
hand_id = id;
};
~CRgroup(){};
shared_ptr<CRgroup> gopen(string group_name){
hid_t group_id = H5Gcreate(hand_id, group_name.c_str(), H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
shared_ptr<CRgroup> tmp = make_shared<CRgroup>(group_id);
return tmp;
};
shared_ptr<CRdata> dataset(string dataset_name){
shared_ptr<CRdata> tmp = make_shared<CRdata>(hand_id, dataset_name);
return tmp;
};
template <class T>
shared_ptr<CRattr> attr(string key, T* value, int len = 1){
shared_ptr<CRattr> tmp = make_shared<CRattr>(hand_id);
tmp->attr<T>(key, value, len);
return tmp;
}
};
/******** FILE ********/
class CRfile
{
private:
hid_t hand_id;
public:
CRfile(string file_name){
hand_id = H5Fcreate(file_name.c_str(), H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
};
~CRfile(){};
shared_ptr<CRgroup> gopen(string group_name){
shared_ptr<CRgroup> tmp = make_shared<CRgroup>(hand_id);
return tmp.gopen(group_name);
};
shared_ptr<CRdata> dataset(string dataset_name){
shared_ptr<CRdata> tmp = make_shared<CRdata>(hand_id, dataset_name);
return tmp;
};
hid_t getHand() {
return hand_id;
}
};
#endif封装的使用示例
struct mtx{
double x;
double y;
string z;
};
struct mt{
double x;
double y;
char* z;
};
struct mtx mtt1[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
mtt1[i].x = i;
mtt1[i].y = i;
mtt1[i].z = "test";
}
struct mt mtt2[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
mtt2[i].x = mtt1[i].x;
mtt2[i].y = mtt1[i].y;
mtt2[i].z = (char*)mtt1[i].z.c_str();
}
double wdata[4] = {1,2,3,4};
Rfile test("test.h5");
struct mt *wdata2 = new struct mt[5];
vector<H5TITLE> title = {{"X","double"},{"Y","double"},{"Z","char"}};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
wdata2[i].x = mtt1[i].x;
wdata2[i].y = mtt1[i].y;
wdata2[i].z = (char*)mtt1[i].z.c_str();
}
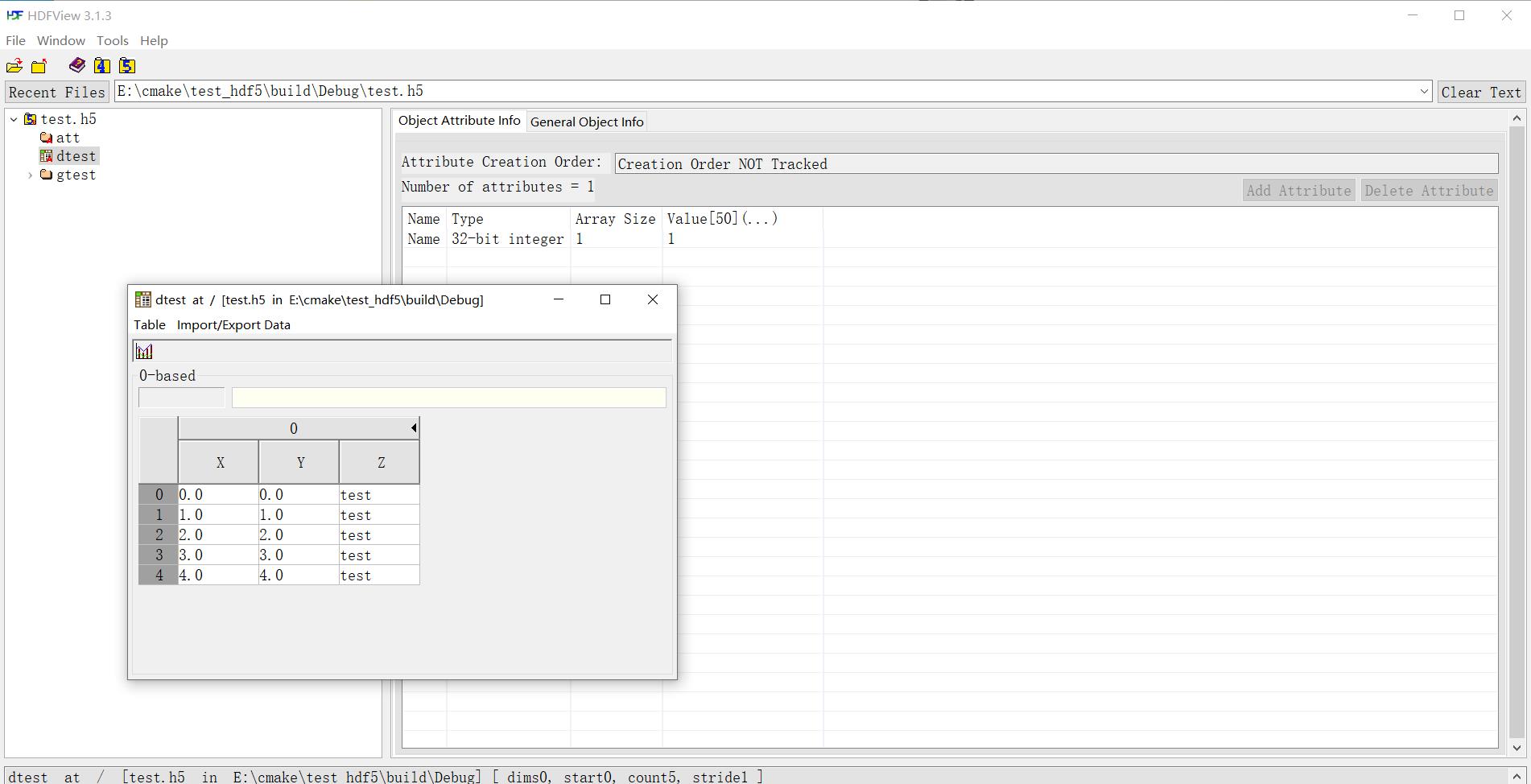
test.gopen("gtest").gopen("gtest2").dataset("dset").insertList<double>(2,2,wdata);
int value[1] = {1};
test.dataset("dtest").insert<mt>(5, wdata2, title).attr<int>("Name", value, 1);
test.gopen("att").attr<int>("test", value, 1).attr<int>("test2", value, 1);图示